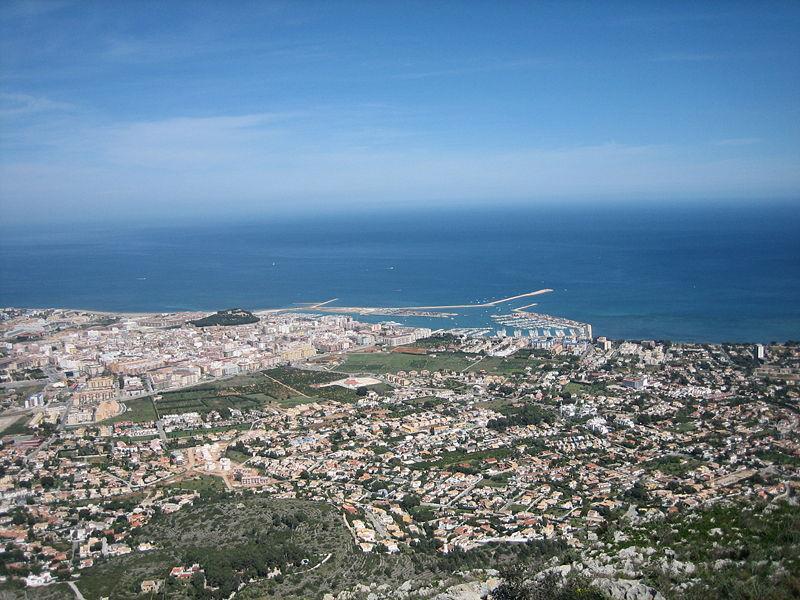
Alicante, Comunidade Valenciana, Spain
Suggest Place to Visit
6428
Track to location with GPS |
 |
Although with archaeological evidence of an Iberian settlement (Diniu), its origin as a city is Roman (Dianium), located to the north of the current city and opposite the old port. The classic texts and archaeological remains indicate that in the 1st century BC. Sertorio's troops established a naval base in Dianium. During the High Empire, the city enjoyed a period of splendor going from being a stipendiary city to a municipality. Between 636 and 693, in times of the Visigothic kingdom, Denia was the episcopal see dependent on Toledo.
Taifa kingdoms in the Iberian peninsula around 1030
In Muslim times, the city reached the climax of its expansion and strength, which generated a moment of great cultural vitality. Daniyya will be the capital of the taifa created in 1010 by the Amiri Muyahid al-Amiri al-Muwaffaq who, by annexing the Balearic Islands, will turn the kingdom into an important maritime and commercial center that will mint its own currency until the Almohad invasion. The taifa lost its independence in 1076, when Iqbal al-Dawla was dethroned by Al-Muqtadir, the hudí king of the Taifa of Zaragoza, on which it depended until the Almoravid invasion (1091).
Denia Castle
The Christian conquest, in 1244, led to a serious setback in the development of the city, practically uninhabited when the Muslim population was removed from it. Repopulated under the jurisdiction of Valencia, the town of Denia, reduced to the bastion of the castle, becomes the center of Christian power in a general term populated mainly by Muslims. Jaime II of Aragon begins the stage of the manorial domain, when he cedes the town in 1298 to Poncio de Ampurias. Later, under the house of Gandía, it became a county (1356), returning to the Crown in the time of Alfonso the Magnanimous. The absenteeism of this monarch made it possible for the lieutenant Juan de Navarra to donate it to the Castilian Diego Gómez de Sandoval y Rojas (1431), with the consequent discontent of the town, who demanded his reincorporation to the kingdom (1455) with the support of the city of Valencia, which occupied the castle until 1477, which included the lands surrounding the city, which are still called the Marquesado. The county remained in the hands of the Sandovals, promoting itself to marquisate in 1487. The Duke of Lerma, fifth Marquis of Denia and favorite of Felipe III, provides the town with important privileges and the title of city. He promoted the expulsion of the Moors (1609), 25,000 of whom embarked in the port of Denia bound for Barbary, with the consequent depopulation and economic ruin of the marquisate.
View of Denia from the northern slope of Montgó
From the 18th century on, the city participated openly in the War of Succession, and was the first to proclaim Archduke Charles king. The war and subsequent reprisals caused the crisis in the city. It was finally occupied by the Bourbons on November 17, 1708. The castle, seriously damaged, will definitely sink in the War of Spanish Independence. In the 19th century, Denia rejoined the Crown (1804) and experienced a gradual growth that began in the fishing district, which became administratively independent between 1837-39. The flourishing trade of the raisin gave rise to a commercial bourgeoisie and attracted foreign companies with the consequent increase in population, which went from 6,538 to 12,413 inhabitants (dianenses) between 1860-1900.
Denia (in Valencian and officially Dénia) is a city in the Valencian Community, Spain. Located on the north coast of the province of Alicante. It is the capital of the Marina Alta region, part of it also known as ´´Marquesado de Denia´´. It has 52,500 inhabitants (INE 2008), in summer its population increases to about 200,000 inhabitants.
Geography [edit]
In addition to the urban center of Denia, there are several districts:
La Jara: located north of the urban center, between Denia and Ondara.
Jesús Pobre: located west of Denia, after Montgó.
La Pedrera: located on the slopes of Montgó.
The Montgó, formerly called Kaón (753 meters above sea level) (Natural Park since 1987) with its majesty dominates the 66.2 km² of the municipality and presents a varied sample of native plants, animals, caves and trails. The other scenic attraction is the Cabo de San Antonio Marine Reserve. This cape has an altitude of 160 m.
Denia is part of the Costa Blanca, which runs from this town to Pilar de la Horadada. It has 20 km of coastline in which the beaches of Les Marines and Las Rotas stand out.
Coves of Denia
Las Rotas beach in Denia.
Bordering towns [edit]
Denia is bordered by the coast to the north with Oliva (in the province of Valencia) and to the south with Jávea (in that of Alicante). To the east it borders the Mediterranean Sea and to the west with various towns: Els Poblets, Vergel, Ondara, Benimeli, Pego, Ráfol de Almunia, Pedreguer, Gata de Gorgos and Teulada.
Accesses [edit]
Denia communicates, by road, with Valencia and Alicante through the N-332 and the AP-7 E-15 Highway (Meditarranean Highway) (Exit 62). It has a bus connection with Gandía, Valencia or Alicante.
It has a railway station on the Denia-Alicante line of F.G.V. (Trenet de la Marina).
It maintains maritime communication with Ibiza (in 2 hours), Palma de Mallorca and Formentera (with the Balearia company).
Distances [edit]
Gandía, 30 km
Benidorm, 63 km
Cullera, 58 km
Alicante, 100 km
Valencia, 100 km
Elche, 120 km
Madrid, 448 km
Barcelona, 445 km
Alicante-´´El Altet´´ Airport, 110 km
Valencia Airport-´´Manises´´, 114 km
You can see that Denia is located in the middle between Alicante and Valencia, but it belongs to the province of Alicante.
Beaches [edit]
Denia has a coastline of 20 km; and the northern beaches are wide and sandy. In the south there are rocky coves. A quality management and environmental management system has been implemented. These beaches are recognized by the ISO 14001 (environmental management) and ISO 9001-2000 (quality management) certificates. It has two beach areas: Las Marinas and Las Rotas.
The Las Marinas area has the sandiest beaches: Cagarritar (the closest to the town), Les Deveses, La Almadraba, Los Molinos, Les Bovetes, Les Marines, Albaranas and Punta Raset.
The Las Rotas area is characterized by its many coves and the promenade (Marineta Casiana, El Trampolín, La Punta Negra, Les Arenetes, La Cala).
Places of interest [edit]
The city is located in a bay or natural port at the foot of the Montgó and shows us old neighborhoods such as Les Roques or Baix la Mar, the streets that go down from the castle remind us of the Arab past of the place and the lower part the modernism that led to the raisin trade. The most interesting museums and monuments are:
Denia street
Old Shipyards. 16th century, modified in the 18th.
Town hall. Neoclassic. Building formed by 6 semicircular arches.
Neighborhoods:
o Barrio Baix la mar: old fishing district.
o Barrio Les Roques: next to the castle.
Calle del Marqués de Campo. It is one of the main streets. Commercial center of the city.
Fortified House. Declared a Site of Cultural Interest (BIC).
Caseta del Pare Pere (´´Padre Pedro´´): example of rural architecture, from the 17th century.
Convent of the Agustinas. 16th and 17th centuries.
Churches:
or Church of the Assumption. Valencian Baroque of the XVIII.
or Church of San Antonio. 16th and 17th centuries. Remodeled in the 18th century.
o Church and Convent of Our Lady of Loreto. Century XVI. Founded by the barefoot Augustinian nuns in 1604.
o Iglesia de Jesús Pobre
o Church of San Mateo de la Jara
Museums:
o Archaeological Museum. Tour of the history of the city. From its Iberian origins to the 18th century. It is located in the Castle of Denia.
o Ethnological Museum. Dedicated to the nineteenth century Dianense and the raisin trade.
o Toy Museum. Denia's toy industry exhibition from 1904 to 1960.
o La Estación Art Center: cultural center where temporary exhibitions are shown.
Reservoirs:
o De la Almadraba: typical Roman maritime town from the 1st to 4th centuries AD.
o Del Alto de Benimaquía: archaic and full Iberian town (6th to 3rd century BC) located on the Montgó.
o Pic de l´Àguila: Iberian town (4th century to 1st century BC) located on Montgó.
Hermitages of the Conquest.
or San Juan. Historic Artistic Monument.
or Santa Paula.
or Saint Lucia. XV century.
The Castle. Built by the Moors on a hill (or tossal) on previous buildings. It has been municipal property since 1952. It houses the Archaeological Museum, an important witness to local history. It has been rehabilitated and is currently open to visitors throughout the year.
Ramparts Some sections are preserved in good condition.
Towers:
o Torre de la Almadraba (or del Palmar): Guaita tower that has undergone a debatable restoration.
o Torre del Gerro (Vase): watchtower with a frustoconical body that gives it its name (vase) due to its shape. The coat of arms of Carlos I XVI century stands out.
o Torre de Carrals. Important set of defensive buildings. Currently privately owned.
Gastronomy and festivals [edit]
Fishermen in the port of Denia
Rice, fish and seafood, especially the world famous boiled Denia red prawn. The seafood casserole (suquet), cakes, espencat, aioli, llandeta, dried octopus, prawns with chard, etc. The mistela and the raisins are the base of an excellent gastronomy, to which we must add the citrus.
As for the festivities, there are Fallas, Bonfires of San Juan, Moros y Cristianos and the peculiar Bous a la Mar.
Comments
We don´t have yet any comments about:
Denia
Denia
Be the first to leave a comment as it is very important to inform other people
Outros locais a visitar
Within a radius of 20 km from:Denia
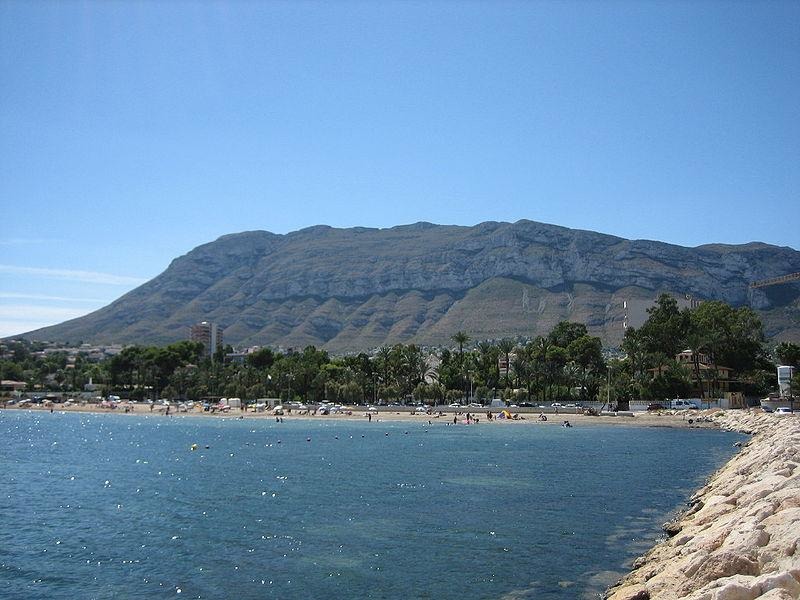
Natural Park of the Macizo del Montgó |
| 3,9 Km |
 |
Javea |
| 5,9 Km |
 |
Benisa |
| 15,2 Km |
 |
Cabo de la Nao (Jávea) |
| 16,2 Km |
 |
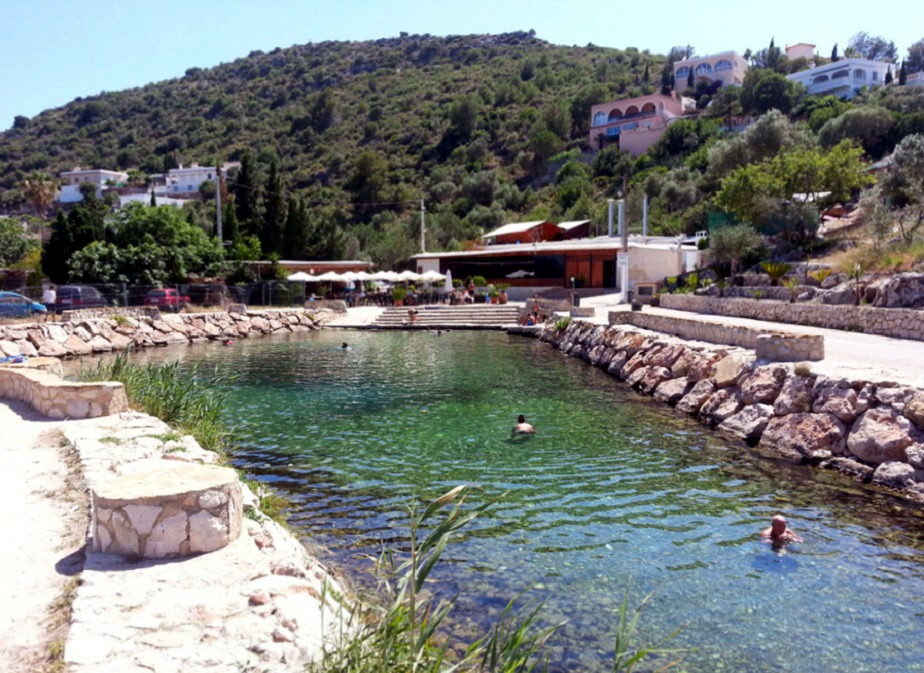
Font Salada or Ullal del Burro |
| 17,4 Km |
 |
Hotel reservation near Denia within a radius of 20 km
Why to book with ROTAS TURISTICAS
The best prices
Our partnerships with the world´s largest operators offer research on the best market prices.
More options
At Rotas Turisticos you can book the hotel, buy the air ticket, book the transfer from the airport to the hotel and vice versa, book the local excursions, rent the car, take travel insurance and consult the places to visit and where to go.
Holiday Tips & Destinations
Hundreds of holiday destinations with all the options that allow you to easily choose the destination that best suits your dream vacation.
ROTAS TURISTICAS
Links